Role of Molecular Sieves in Insulating Glass
The application of molecular sieves in insulating glass is crucial for maintaining its thermal insulation, soundproofing, and aesthetic performance.
Insulating glass, as an efficient building energy-saving material, is widely used in modern construction due to its excellent thermal insulation and soundproofing properties. Molecular sieves, as a key component of insulating glass, play a crucial role in maintaining its performance. This article will explore the application of molecular sieves in insulating glass and their importance.
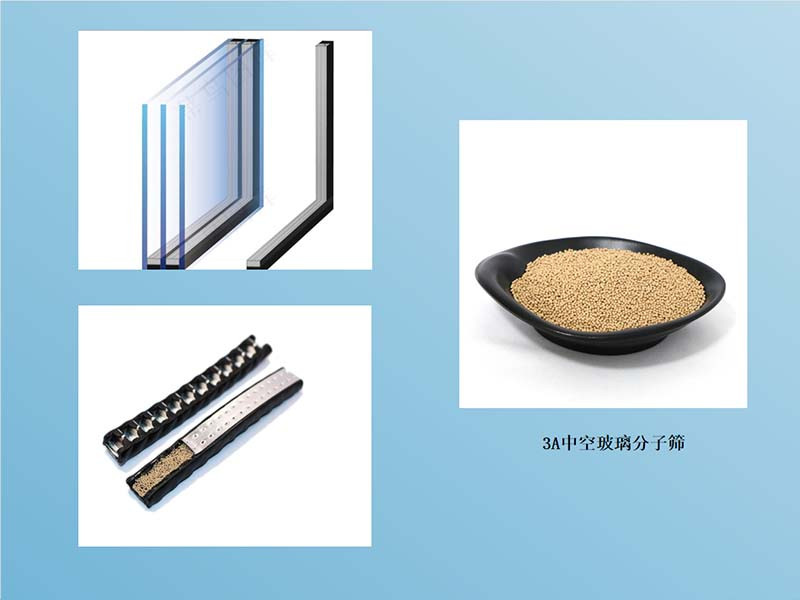
Basic Function of Molecular Sieves
Molecular sieves are materials with a highly ordered microporous structure that selectively adsorb gas molecules based on their size and polarity. In insulating glass, molecular sieves are mainly used to adsorb moisture and certain organic vapors in the sealed air or gas, thereby keeping the interior environment of the insulating glass dry.
Role of Molecular Sieves in Insulating Glass
Preventing Fogging and Condensation: Molecular sieves absorb moisture in the internal air, preventing fogging and condensation inside the insulating glass and maintaining a clear view.
Extending Service Life: By maintaining a dry environment, molecular sieves help extend the sealed life of insulating glass and reduce corrosion and seal failure caused by humidity.
Enhancing Insulation Performance: Molecular sieves help maintain the dryness of the gas layer, thereby optimizing the insulating performance of the insulating glass.
Improving Soundproofing Effect: A dry gas layer can provide better acoustic performance; molecular sieves ensure the soundproofing effect is not affected by absorbing moisture.
Types and Selection of Molecular Sieves

Common types of molecular sieves used in insulating glass include Type 3A and Type 4A. Factors to consider when selecting include:
Adsorption Capacity: Choose a molecular sieve with appropriate adsorption capacity based on the design and expected service life of the insulating glass.
Pore Size: The pore size of the molecular sieve affects its ability to adsorb specific molecules. Choose the right pore size to meet specific needs.
Temperature Stability: Molecular sieves need to remain stable within the temperature range used for insulating glass.
Regenerability: Choose molecular sieves with good regenerability so that they can recover their function after becoming saturated with adsorbates.
Conclusion
The application of molecular sieves in insulating glass is crucial for maintaining its thermal insulation, soundproofing, and aesthetic performance. With increasing demands for building energy efficiency, molecular sieves, as an efficient and environmentally friendly material, will find broader application in the manufacture of insulating glass. Manufacturers and designers need to carefully select the appropriate type of molecular sieve to ensure the quality and performance of the final product.





